SSH Remote IoT Device Example: Securely Access Your Gadgets Today
Connecting to your smart devices, sensors, or little computers from a distance can feel like magic, but it's really about having the right tools. Secure Shell, or SSH, is that tool for many folks who work with Internet of Things (IoT) gadgets. It gives you a safe way to talk to your devices, no matter where you are, which is pretty handy. This means you can check on things, send new instructions, or fix problems without actually being right there with your device.
Think about a tiny computer, maybe a Raspberry Pi, sitting in your garden collecting weather data. You might want to get that data, or perhaps tell it to start measuring something else. Walking out to the garden, plugging in a monitor and keyboard, that's just not practical, is it? SSH lets you do all of that from the comfort of your desk, or even from another city, which is quite convenient.
This article will walk you through how SSH makes this possible. We'll look at setting things up, what to do when you hit a snag, and some simple ways to move files around. So, you can feel more confident about managing your connected devices, more or less, with ease.
- Securely Connect Remoteiot Vpc Raspberry Pi Aws Server
- 4 Guard Buzz Cut
- Twin Where Have You Been
- Remoteiot P2p Download
- How Many Children Does Pam Bondi Have
Table of Contents
- What is SSH and Why Your IoT Device Needs It
- Getting Ready: Preparing Your IoT Device for Remote Access
- Creating Your Digital Keys: SSH Key Authentication
- Connecting From Afar: Your First Remote SSH Session
- Handling Files Remotely: SCP for Your IoT Projects
- When Things Go Sideways: Common SSH Troubles
- Staying Connected: Keeping Your IoT Link Stable
- Frequently Asked Questions About SSH and IoT
- Taking the Next Step with Your Connected Devices
What is SSH and Why Your IoT Device Needs It
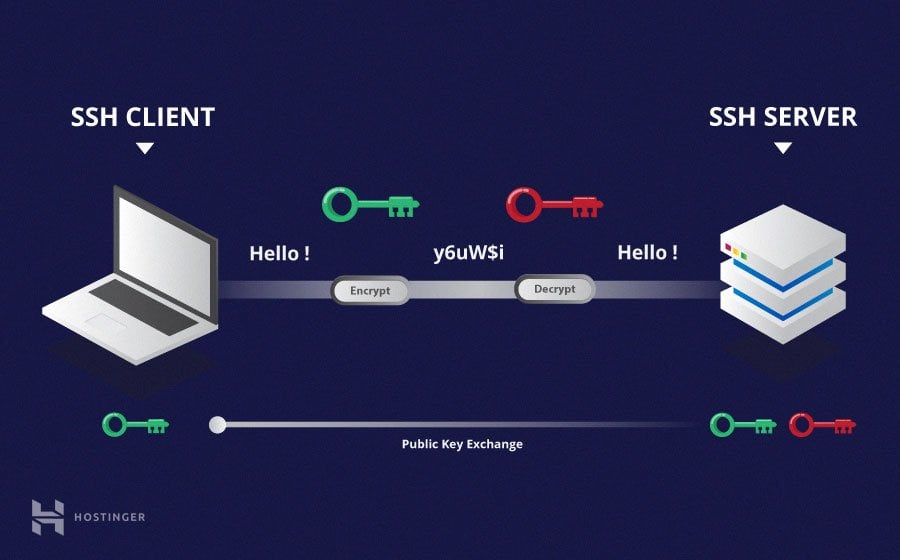
SSH, or Secure Shell, is a network way to connect to another computer safely. It's like having a very secure phone line directly to your IoT device. This connection is encrypted, which means that whatever information you send back and forth, it stays private. Nobody else can easily listen in on your conversation with your device, which is very important for security.
The Security Blanket for Your Connected Things
Your IoT devices, whether they are smart sensors or tiny home servers, are often connected to the internet. This makes them, arguably, open to unwanted visitors if they aren't protected. SSH acts as a strong barrier, making sure only authorized people can get in. It's a way to make sure your data is safe and your device isn't used for something it shouldn't be, which is pretty good.
Why Not Just Use a Password?
While passwords are a start, they can sometimes be guessed or cracked. SSH offers a more robust method: key authentication. This involves two special files, a public key and a private key. It's like having a lock and a key, where the lock (public key) is on your device, and only your specific key (private key) can open it. This makes it much harder for someone to break in, so, it's a better choice for security.
- Steve Horstmeyer Dogs
- Bianca Censori Before Kanye
- Wasmo Somali Chanel
- Me Too In Spanish
- Do A Barrel Barrel Roll
Getting Ready: Preparing Your IoT Device for Remote Access
Before you can connect, your IoT device needs to be ready. This usually means it has an operating system installed, like a version of Linux, and the SSH server software is running. For many small devices, especially those like a Raspberry Pi, this setup is quite common, you know, and relatively simple.
Picking the Right Device (Like a Raspberry Pi)
Many IoT projects use devices like the Raspberry Pi because they are small, powerful enough, and can run a full operating system. These devices typically come with SSH capabilities built in or are very easy to set up for it. They are, in a way, a great choice for learning about remote access because of their widespread use and community support.
Enabling SSH on Your Device
For a Raspberry Pi, you can usually enable SSH through a configuration tool or by simply placing a file named `ssh` (with no extension) on the boot partition of the SD card before you start it up. After getting sudo privileges, you might use a command like `sudo systemctl enable ssh` and `sudo systemctl start ssh` to make sure the SSH server is running. This makes the device listen for incoming connections, which is sort of how it begins to work.
Creating Your Digital Keys: SSH Key Authentication
Using SSH keys is a much safer way to connect than just relying on passwords. It means you don't have to type a password every time, and it's far more secure. This process involves creating a pair of digital keys on your computer, which is actually quite straightforward.
Making Your Own Key Pair
You can create these keys right from your computer's terminal. A common command for this is `ssh-keygen`. It will ask you where to save the keys and if you want a passphrase for extra protection. Having a passphrase is a good idea, as it adds another layer of security to your private key, which is very helpful.
Copying Your Public Key to the Device
Once you have your key pair, you need to get the public key onto your IoT device. A tool called `ssh-copy-id` can do this automatically. If that's not available, you can manually copy it. My text mentions, "In terminal enter this command with your ssh file name `pbcopy < ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub` this will copy the file to your clipboard now open you github account go to settings > ssh and gpg keys >." While this example points to GitHub, the idea is the same for your IoT device: get that public key onto the device's authorized keys file. This tells your device to trust connections from your computer, which is pretty neat.
Connecting From Afar: Your First Remote SSH Session
With your device ready and keys in place, you are now set to connect. This is where you really start to feel the benefit of SSH. It's like having a direct line to your device, even if it's across the room or across the globe, so, it's quite powerful.
The Simple Command to Connect
To connect, you just open your terminal and type `ssh username@device_ip_address`. Replace `username` with the user account on your IoT device (often `pi` for a Raspberry Pi) and `device_ip_address` with its network address. If you're using SSH keys, it should connect without asking for a password, which is really convenient. For example, `ssh pi@192.168.1.100` might be your command.
What if It Doesn't Connect?
Sometimes, things don't go as planned. You might get an error like "Could not resolve hostname node01" if your computer can't find the device on the network. This means the name you typed isn't matching an IP address, or the device isn't online. Double-check the IP address or hostname. Also, make sure the device is actually powered on and connected to the network, because, you know, that's important.
Handling Files Remotely: SCP for Your IoT Projects
SSH isn't just for running commands; it's also great for moving files. SCP, or Secure Copy Protocol, uses SSH to transfer files securely between your computer and your IoT device. This is super useful for sending new scripts, getting data logs, or updating software, which is very practical.
Moving Files Back and Forth
The `scp` command works similarly to `ssh`. To copy a file from your computer to the device, you might use `scp /path/to/local/file username@device_ip_address:/path/on/device`. To copy from the device to your computer, you just swap the source and destination. It's a fairly simple way to manage your files remotely, more or less.
A Little Example of Transferring a Folder
My text mentions, "I try to transfer a folder of files from my local computer to a server via ssh and scp." To do this, you'd use the `-r` option with `scp` for "recursive," which tells it to copy folders and their contents. So, `scp -r /path/to/local/folder username@device_ip_address:/path/on/device` would move an entire folder. This makes it very easy to manage entire project directories on your remote device, which is quite handy.
When Things Go Sideways: Common SSH Troubles
Even with careful setup, you might run into issues. It's part of working with technology, and knowing some common problems and their fixes can save you a lot of frustration. These little hiccups are, you know, just part of the process.
"Remote Script Returns 255"
My text notes, "For some reason your remote script returns 255, and ssh just delivers its result to you." A return code of 255 often means a general error or that the script you tried to run on the remote device exited with an error. This isn't an SSH connection problem itself, but rather an issue with the command or script you executed. You might need to check the script for errors, or see what it's trying to do, so, that's where you'd look.
"Invalid Host for SSH Forwarding"
This error, "Error invalid host for ssh forwarding," suggests a problem with how you've set up SSH forwarding, perhaps for a feature like X11 or port forwarding. It means the host you're trying to forward to isn't recognized or is incorrectly specified in your SSH configuration. You might need to check your `~/.ssh/config` file or the command line arguments you're using for forwarding, which is pretty specific.
"Could Not Resolve Hostname"
As mentioned earlier, "Could not resolve hostname node01" means your system can't turn the name `node01` into an IP address. This could be a typo, the device might be offline, or your network's DNS (Domain Name System) isn't working right. Verify the hostname or use the device's IP address directly. Sometimes, a simple network restart can fix this, you know, for some reason.
X11 Forwarding Headaches
My text states, "If you run ssh and display is not set, it means ssh is not forwarding the x11 connection." And, "To confirm that ssh is forwarding x11, check for a line containing requesting x11 forwarding in the output of." X11 forwarding lets you run graphical applications from your IoT device and display them on your local computer. If it's not working, make sure you used the `-X` option with your SSH command (e.g., `ssh -X username@device_ip_address`) and that the X11 server is set up on both ends. This is a bit more involved, but, it's very useful for graphical tasks.
Authentication Woes After Password Changes
My text shares, "I met this issue after i changed my apple id password, so i updated my apple id and restarted my mac." While this specifically mentions an Apple ID, the general problem of authentication failing after a password change can happen with SSH too. If you're using password authentication for SSH and you change the device's user password, you'll need to use the new password. If you're using SSH keys and they suddenly stop working, it might be an issue with permissions on your key files or how they are added to your SSH agent. Sometimes, regenerating keys or carefully checking permissions helps, which is pretty common.
Another point from my text, "After installing git on my new work computer, generating my ssh key and adding it on gitlab, i'm trying to clone a project but i get the following error." This is a similar authentication issue, but specifically with Git and GitLab. The fix often involves making sure your SSH key is correctly added to your Git service and that your local SSH agent is aware of your private key. It's all about making sure the digital handshake happens correctly, which, you know, is basically how it works.
Finally, my text mentions, "Our team has successfully installed an ubuntu server 22.04.3 lts with the openssh server package included, Open the /etc/ssh/ssh_config and remove all the listed options, They are supposed to be part of the sshd_config (the server configuration), not the client one." This is a key point: `ssh_config` is for your client (your computer), and `sshd_config` is for the server (your IoT device). Putting server options in the client config will cause problems. Always make sure you're editing the correct file for what you intend to do, because, that's just how it goes.
Staying Connected: Keeping Your IoT Link Stable
Sometimes, SSH connections can freeze or drop. My text says, "Unfortunately, terminal freezes in 10." This can be due to network instability, inactivity timeouts, or even issues on the remote device itself. Using SSH keep-alive options in your client configuration can help. You can add lines like `ServerAliveInterval 60` to your `~/.ssh/config` file. This sends a small message to the server every 60 seconds to keep the connection active, which is a bit like tapping on the glass to see if the fish are still there.
My text also points out, "It is always connected and works properly when i am in the work place." This suggests a network-specific issue. Your home network or public Wi-Fi might have different firewall rules or stability than your workplace network. Checking your router settings or trying a different network connection can help pinpoint the problem, which, you know, can be tricky to figure out.
Frequently Asked Questions About SSH and IoT
Here are some common questions people ask about using SSH with their IoT devices:
How do I find my IoT device's IP address for SSH?
You can often find your device's IP address by logging into your router's administration page, which usually lists all connected devices. On the device itself, if you have a display, you might use a command like `ifconfig` or `ip a`. Sometimes, network scanning tools can also help you discover devices on your network, which is very useful.
Is SSH secure enough for sensitive IoT data?
Yes, SSH provides strong encryption for the connection itself. However, the overall security of your sensitive IoT data also depends on other factors, like how secure your device's operating system is, if you're using strong passwords or, even better, SSH keys, and how you're handling the data once it's on your device. It's a bit like a chain, and every link needs to be strong.
Can I access my IoT device via SSH when I'm away from home?
Absolutely, yes! This is one of the biggest benefits of SSH for IoT. You'll need to set up port forwarding on your home router to direct incoming SSH requests to your IoT device's local IP address. Be very careful with this step, as it opens a port on your home network to the internet. Make sure your SSH setup is very secure with key authentication, because, you know, security matters a lot here.
Taking the Next Step with Your Connected Devices
Getting comfortable with SSH for your IoT devices opens up a whole new world of possibilities. You can manage them from anywhere, automate tasks, and keep your projects running smoothly and safely. It's a fundamental skill for anyone playing with connected technology. So, you can learn more about secure remote access on our site, and perhaps, link to this page for more details on OpenSSH, which is pretty helpful.
Remember, the key to successful remote management is patience and a willingness to troubleshoot. You might encounter issues like those mentioned, for example, problems with SSH keys or network settings. Keep practicing, and you'll soon be a pro at managing your IoT fleet from afar, which is really quite something.
- Whats Jon Gruden Doing Now
- Moth Grow A Garden
- Filmy Fly Com
- What Does Yeet Mean
- Emily Compagno Husband
SSH Tutorial: What is SSH, Encryptions and Ports

What Is SSH? | How to Use SSH (Secure Shell) | Gcore

Windows SSH Server | Learning, Secure shell, Software engineer